Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
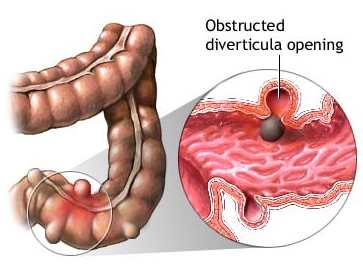
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots, like an inner tube that pokes through weak places in a tire. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. Pouches (plural) are called diverticula. The condition of having diverticula is called diverticulosis. About 10 percent of Americans over the age of 40 have diverticulosis. The condition becomes more common as people age. About half of all people over the age of 60 have diverticulosis.
When the pouches become infected or inflamed, the condition is called diverticulitis. This happens in 10 to 25 percent of people with diverticulosis. Diverticulosis and diverticulitis are also called diverticular disease.
Illustration of the colon (large intestine) and an enlargement of it showing diverticula.
What are the symptoms?
Diverticulosis
Most people with diverticulosis do not have any discomfort or symptoms. However, symptoms may include mild cramps, bloating, and constipation. Other diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and stomach ulcers cause similar problems, so these symptoms do not always mean a person has diverticulosis. You should visit your doctor if you have these troubling symptoms.
Diverticulitis
The most common symptom of diverticulitis is abdominal pain. The most common sign is tenderness around the left side of the lower abdomen. If infection is the cause, fever, nausea, vomiting, chills, cramping, and constipation may occur as well. The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of the infection and complications.
What are the complications?
Diverticulitis can lead to bleeding, infections, perforations or tears, or blockages. These complications always require treatment to prevent them from progressing and causing serious illness.
Bleeding
Bleeding from diverticula is a rare complication. When diverticula bleed, blood may appear in the toilet or in your stool. Bleeding can be severe, but it may stop by itself and not require treatment. Doctors believe bleeding diverticula are caused by a small blood vessel in a diverticulum that weakens and finally bursts. If you have bleeding from the rectum, you should see your doctor. If the bleeding does not stop, surgery may be necessary.
Abscess, Perforation, and Peritonitis
The infection causing diverticulitis often clears up after a few days of treatment with antibiotics. If the condition gets worse, an abscess may form in the colon. An abscess is an infected area with pus that may cause swelling and destroy tissue. Sometimes the infected diverticula may develop small holes, called perforations. These perforations allow pus to leak out of the colon into the abdominal area. If the abscess is small and remains in the colon, it may clear up after treatment with antibiotics. If the abscess does not clear up with antibiotics, the doctor may need to drain it.
A large abscess can become a serious problem if the infection leaks out and contaminates areas outside the colon. Infection that spreads into the abdominal cavity is called peritonitis. Peritonitis requires immediate surgery to clean the abdominal cavity and remove the damaged part of the colon. Without surgery, peritonitis can be fatal.
Fistula
A fistula is an abnormal connection of tissue between two organs or between an organ and the skin. When damaged tissues come into contact with each other during infection, they sometimes stick together.If they heal that way, a fistula forms. When diverticulitis-related infection spreads outside the colon, the colon's tissue may stick to nearby tissues. The organs usually involved are the bladder, small intestine, and skin.
The most common type of fistula occurs between the bladder and the colon. It affects men more than women. This type of fistula can result in a severe, long-lasting infection of the urinary tract. The problem can be corrected with surgery to remove the fistula and the affected part of the colon.
Intestinal Obstruction
The scarring caused by infection may cause partial or total blockage of the large intestine. When this happens, the colon is unable to move bowel contents normally. When the obstruction totally blocks the intestine, emergency surgery is necessary. Partial bstruction totally blocks the intestine, emergency surgery is necessary. Partial blockage is not an emergency, so the surgery to correct it can be planned.
What causes diverticular disease?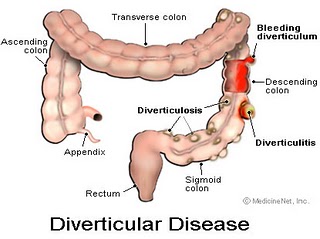 Although not proven, the dominant theory is that a low-fiber diet is the main cause of diverticular disease. The disease was first noticed in the United States in the early 1900s. At about the same time, processed foods were introduced into the American diet. Many processed foods contain refined, low-fiber flour. Unlike whole-wheat flour, refined flour has no wheat bran.
Although not proven, the dominant theory is that a low-fiber diet is the main cause of diverticular disease. The disease was first noticed in the United States in the early 1900s. At about the same time, processed foods were introduced into the American diet. Many processed foods contain refined, low-fiber flour. Unlike whole-wheat flour, refined flour has no wheat bran.
Fiber is the part of fruits, vegetables, and grains that the body cannot digest. Some fiber dissolves easily in water (soluble fiber). It takes on a soft, jelly-like texture in the intestines. Some fiber passes almost unchanged through the intestines (insoluble fiber). Both kinds of fiber help make stools soft and easy to pass. Fiber also prevents constipation.
Constipation makes the muscles strain to move stool that is too hard. It is the main cause of increased pressure in the colon. This excess pressure might cause the weak spots in the colon to bulge out and become diverticula.
Diverticulitis occurs when diverticula become infected or inflamed. Doctors are not certain what causes the infection. It may begin when stool or bacteria are caught in the diverticula. An attack of diverticulitis can develop suddenly and without warning.
How does the doctor diagnose diverticular disease?
To diagnose diverticular disease, the doctor asks about medical history, does a physical exam, and may perform one or more diagnostic tests. Because most people do not have symptoms, diverticulosis is often found through tests ordered for another ailment.
When taking a medical history, the doctor may ask about bowel habits, symptoms, pain, diet, and medications. The physical exam usually involves a digital rectal exam. To perform this test, the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to detect tenderness, blockage, or blood. The doctor may check stool for signs of bleeding and test blood for signs of infection. The doctor may also order x rays or other tests.
What is the treatment for diverticular disease?
A high-fiber diet and, occasionally, mild pain medications will help relieve symptoms in most cases. Sometimes an attack of diverticulitis is serious enough to require a hospital stay and possibly surgery.
Diverticulosis
Increasing the amount of fiber in the diet may reduce symptoms of diverticulosis and prevent complications such as diverticulitis. Fiber keeps stool soft and lowers pressure inside the colon so that bowel contents can move through easily. The American Dietetic Association recommends 20 to 35 grams of fiber each day. The table below shows the amount of fiber in some foods that you can easily add to your diet.
Amount of Fiber in Some Foods
| Fruits | Grams |
| Apple, raw, with skin | 3,3 |
| Peach, raw | 1,5 |
| Pear, raw | 5,1 |
| Tangerine, raw | 1,9 |
| Vegetables | |
| Asparagus, fresh, cooked | 1,2 |
| Broccoli, fresh, cooked | 2,6 |
| Brussels sprouts, fresh, cooked | 2 |
| Cabbage, fresh, cooked | 1,5 |
| Carrot, fresh, cooked | 2,3 |
| Cauliflower, fresh, cooked | 1,7 |
| Romaine lettuce | 2,2 |
| Spinach, fresh, cooked | 2,5 |
| Tomato, raw | 1 |
| Winter squash, cooked | 6,3 |
| Grains | |
| Bread, whole-wheat | 1,9 |
| Brown rice, cooked | 3,5 |
| Cereal, bran flake | 5,3 |
| White rice, cooked | 0,6 |
The doctor may also recommend taking a fiber product such as Citrucel or Metamucil once a day. These products are mixed with water and provide about 2 to 3.5 grams of fiber per tablespoon, mixed with 8 ounces of water.
Avoidance of nuts, popcorn, and sunflower, pumpkin, caraway, and sesame seeds has been recommended by physicians out of fear that food particles could enter, block, or irritate the diverticula. However, no scientific data support this treatment measure. Eating a high-fiber diet is the only requirement highly emphasized across the literature and eliminating specific foods is not necessary. The seeds in tomatoes, zucchini, cucumbers, strawberries, and raspberries, as well as poppy seeds, are generally considered harmless. People differ in the amounts and types of foods they can eat. Decisions about diet should be made based on what works best for each person. Keeping a food diary may help identify individual items in one's diet.
If cramps, bloating, and constipation are problems, the doctor may prescribe a short course of pain medication. However, many medications affect emptying of the colon, an undesirable side effect for people with diverticulosis.
Diverticulitis
Treatment for diverticulitis focuses on clearing up the infection and inflammation, resting the colon, and preventing or minimizing complications. An attack of diverticulitis without complications may respond to antibiotics within a few days if treated early.
To help the colon rest, the doctor may recommend bed rest and a liquid diet, along with a pain reliever.
An acute attack with severe pain or severe infection may require a hospital stay. Most acute cases of diverticulitis are treated with antibiotics and a liquid diet. The antibiotics are given by injection into a vein. In some cases, however, surgery may be necessary.
When is surgery necessary?
If attacks are severe or frequent, the doctor may advise surgery. The surgeon removes the affected part of the colon and joins the remaining sections. This type of surgery, called colon resection, aims to keep attacks from coming back and to prevent complications. The doctor may also recommend surgery for complications of a fistula or intestinal obstruction.
If antibiotics do not correct an attack, emergency surgery may be required. Other reasons for emergency surgery include a large abscess, perforation, peritonitis, or continued bleeding.
Emergency surgery usually involves two operations. The first surgery will clear the infected abdominal cavity and remove part of the colon. Because of infection and sometimes obstruction, it is not safe to rejoin the colon during the first operation. Instead, the surgeon creates a temporary hole, or stoma, in the abdomen. The end of the colon is connected to the hole, a procedure called a colostomy, to allow normal eating and bowel movements. The stool goes into a bag attached to the opening in the abdomen. In the second operation, the surgeon rejoins the ends of the colon.